Two new forces are introduced when discussing nuclear phenomena: So its range is only a few femtometers. The forces reach up to half a million newtons within a space smaller than an atomic nucleus.
class 8 Force And Pressure Short notes science chapter 11 Reliable
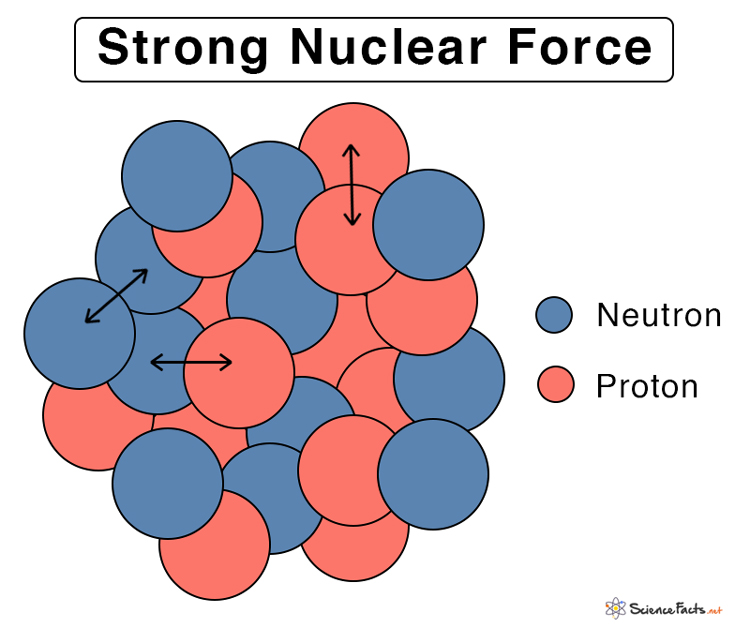
There are several forces acting on the particles (nucleons) inside an atomic nucleus:
The and the weak nuclear force.
There are two types of forces operating inside the nucleus of an atom. This is the force that holds the protons and neutrons together in the nucleus. At this point, you are likely familiar with the neutron and proton, the two fundamental particles that make up the nucleus of an atom. Nuclear forces (also known as nuclear interactions or strong forces) are the forces that act between two or more nucleons.
They bind protons and neutrons (“nucleons”). When two protons encounter each other, they experience all four of the. The force which a charged particle exerts on another charged particle is called. The strong and weak interactions.

These findings enhance understanding of proton dynamics, potentially impacting.
Within an atom's nucleus, two fundamental forces play crucial roles: This force is responsible for binding protons and. Nuclear forces (also known as nuclear interactions) are the forces that act between two or more nucleons. The strong force acts solely within the nucleus.
There are two main forces that act on particles in the nucleus of an atom: Nuclear forces, also known as nuclear interactions, are the forces that act between two or more nucleons. They bind protons and neutrons ( together called nucleons) into the atomic nuclei. These forces have specific distances, or ranges, over which they are felt.

They bind protons and neutrons into atomic nuclei.
The strong nuclear force, and the. Those two particles, collectively called nucleons, make up.